Internationalization is a normal process and today every company needs to think globally. When you have already reached top positions in your homeland, your business can only expand in other countries and the best way to gain new customers is to translate your website.
However, in terms of web development and design, multilingual sites demand a bit more than mere translation. In fact, multilingual websites are beyond just words and their equivalents and designers often forget that they need to adjust them to a whole different culture and customs.
In order to avert disaster and protect your company’s reputation in a foreign country, here are eight tips for eschewing typical mistakes in web design and development on multilingual websites.
The Most Frequent Mistakes In Multilingual Web Design and Development (and how to avoid them):
1. Machine translation
Even though not so technical a mistake, the first problem designers and developers encounter is text translation. Sometimes clients expect the web design agency to provide them with 45 language translations and avoid extra costs, so designers – out of fear or some other reason – want to fill the gap in the design and turn to Google Translate. This must never be done. Designers may know design or coding, but they are not experts in translation and cannot evaluate if a translation is good or bad. Even though machine translation is in a phase where it can produce some good translations of individual words, in the majority of cases where sensitive information and culture-awareness is needed, it can do little to nothing.

Solution:
Hire a real person. An experienced translator. Translators are people of flesh and blood, educated and trained to produce an accurate and appropriate translation. Their role is not mere scribbling or retyping words in a different language – their job is to bridge the gap between two cultures and make connections when there are none. Natural language can be processed only by a living being, And remember to never go for the cheapest option, because this may cost you the most in the long run: you can offend your potential business partners and lose your position in a foreign market for good.
2. Language options misplacement
If your visitors come to your website and they come from a different country, they will probably look for a button to change the language. However, if they cannot find it easily, the odds are that they will instantly leave. To avoid this, in the design process you must find the right spot to place a language picker. Firstly, you need to think of the icons: should you use language or flags? Best practice would be to use the name of the language, and if you want to highlight the variant (such as Australian English, Canadian English, Swiss German or Catalan Spanish) you can also add the flag next to the name of the language (e.g. it is better to use Deutsch rather than German). Secondly, there are many places you can put the language button, but only one or two are the right ones, and it depends on the writing direction and general organization of your web page.
Solution:
In LTR languages, this button is usually placed in the right upper corner so that visitors can see it the moment they enter your website. On the other hand, in RTL languages, the button is placed in the left upper corner of the website. When there are many languages available on your website, you can use a drop-down menu which enlists them all. However, the position of the language picker can differ according to website purpose. For example, if your website is an informative one and you want to let visitors know that there are different versions of your page, you can place the picker in the left sidebar, just like Wikipedia did. People are so accustomed to this position that they instantly look for language options in this position on other encyclopedic websites as well.
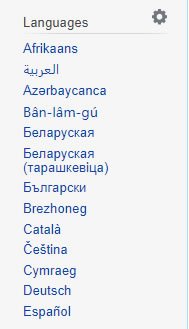
There is also the option of automatic language detection, which implies that your website recognizes the visitor’s location and chooses the language on its own. Just ask your web developer to perform this on your website.
3. No culture awareness
As previously highlighted, translators are mediators between cultures, and it is their job to connect people from different parts of the world. When two people from different cultures meet, they need to learn one another’s customs. In terms of design, this means adapting all the design elements to the needs of the target culture. But how not to offend someone from a different culture?
Solution:
The right answer to this question is to research. Find out what the customs of the country are and try to go with neutral principles. For example, in the west it is normal for people to use images of women in T-shirts and with hair flowing around; however, in the east, this may seem offensive since their women are protected from the eyes of foreigners. If you want to respect your target country’s customs, you will accept this and adjust your design accordingly. Similarly, color psychology and color theory also depend on culture and customs. In the west, it is normal for people to use blue for IT companies; on the other hand, in the east (e.g. in Korea or Mexico), blue is the color of mourning.
4. Content organization
Organization of content on your multilingual website is one of the most important elements in web design. It largely depends on the writing system, i.e. direction. For example, if you come from an English or Spanish-speaking country, where people read and write from left to right (LTR), it may surprise you to see a mirror image of the menu and other website elements in an Arabic or Hebrew website.
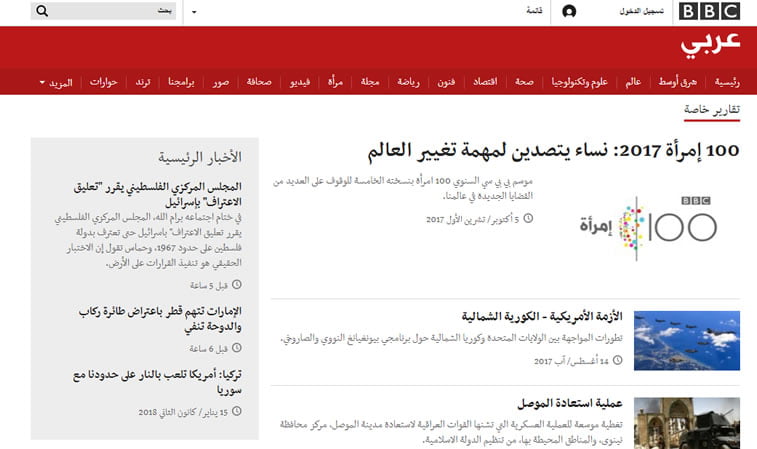
Solution:
That is right, in countries where people write from right to left (RTL) such as Israel, Iran, Afghanistan or Pakistan, websites look differently to adjust to their needs, so the menu will also give you options and links in an RTL direction. Likewise, the organization of elements in these websites will also be different, so you will have to put the language option in the left top corner of the site and menu in a mirror image of a western website. So, before you start redesigning your multilingual website, you should check your target country’s script direction on the w3 website.
5. Encoding and special characters
Similarly to writing direction, a website’s language can be written in different scripts with special characters (such as č, ć, ž, đ, š for Slavic languages which use the Latin alphabet, or Cyrillic alphabet which is used in Russian, Bulgarian, Serbian and Azerbaijan websites) which demand the use of special encoding and fonts which support them.

Solution:
It is quite simple: if you want all characters to be shown properly, use UTF-8 character encoding in the head of the page: <meta charset=”utf-8″>. This Unicode-based encoding supports many languages and can accommodate them even when there is a mixture of different languages in one and the same page. Likewise, the font you are using must be adapted to hundreds of different characters that non-Latin scripts use, so you need to find alternatives on the Google Fonts website.
6. Duplicate content
Duplicate content is an SEO issue and Google will punish you for having it on your website. Duplicate content issues occur when someone forgets to translate all the web page elements and content, so they remain written in the source language, which Google sees as duplicate content and then penalizes your page for it.

Solution:
To solve this problem, your developer or SEO specialist should identify a preferred language variety for each location and/or language. So, for example, if you have the same content for Australian, Canadian and British websites, your developer should assign a <link rel=”alternate” href=”example.com” hreflang=”en-uk” /> or en-au or en-nz alternatives for each location. This head element will tell Google or other search engines that the variation is used for English speakers living in the UK (or Australia, or New Zealand, respectively), and will give them a proper ranking in the local search engine.
7. Dates and orthography
Dates and orthography are important because they vary across the world. For example, if you schedule a promotion on April 1, 2018 – this date will look differently in Europe and in the USA. The French write their dates in the following format: day/month/year, whereas the Americans switch month and day: month/day/year. Not knowing this can lead to completely different results, so if you set a date for 4/1/2018, the French audience will understand this as January 4, whereas the Americans – as April 1. Likewise, orthography – such as decimal marks are of great importance and are not the same in all countries. In the USA, a decimal separator is usually a dot (35.46), whereas the EU uses a comma (35,46).
Solution:
To avoid this, learn or Google what date formats and other orthographic principles apply for your target country and use them consistently throughout the website to avoid confusion. If you want people from abroad to call you, you also need to provide them with your country code.
8. No word of SEO
In the end, it all comes down to search engine optimization. When web design and development are done, an SEO expert should adapt your website to the rules of the biggest algorithm on the planet. If you fail to do local SEO on your multilingual website, the results will never come.

Solution:
It is best to hire an SEO agency or an expert to go through your website code in every language you have on your website and adjust it to the rules of the local search engine. Without this, there is no use even having a website if it cannot be found on Google.
Back to you: what do you think are the worst mistakes that can happen in terms of web design and development of multilingual websites? Tell us in the comments below.





